WhisperGate

Table of content⌗
Introduction⌗
On 05.01.2022, Ukrain had to face a massive cyber attack. This attack was able to take down IT infrastructure of several organizations completely.
Microsoft incident response team recently released samples of malware used in the campaign.
Samples⌗
Environment⌗
Windows 10 guest (Virtualbox)
Windows 10 host
Tools⌗
IDA
x32dbg
bochs
Analysis⌗
Behavioral analysis⌗
malware needs administrative privileges in order to be successful.

Malware does not create any network traffic, registry modifications or file modifications
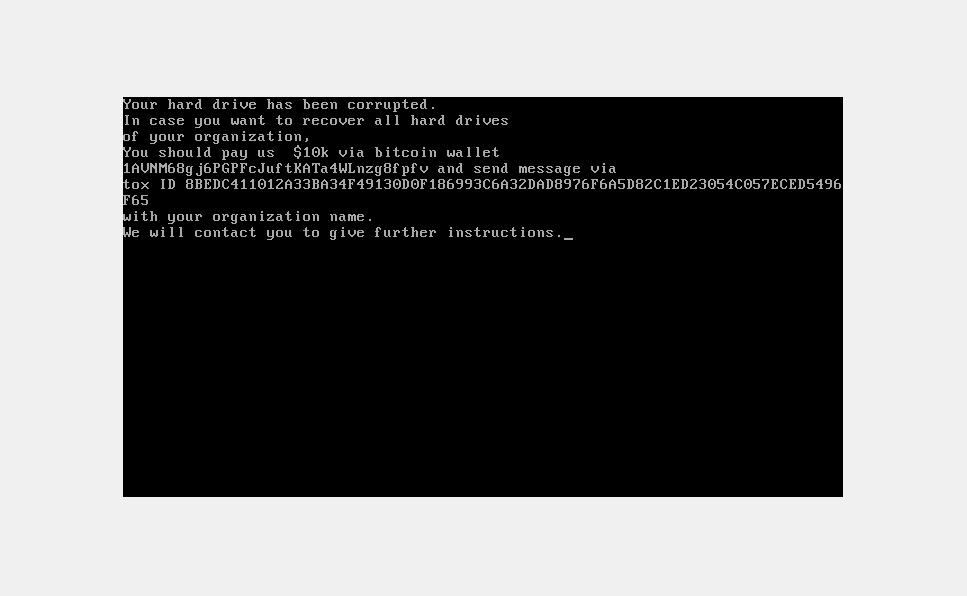
Upon restarting, device will boot into a screen displaying the following ransom note.
Static analysis⌗
The PE⌗
According to detect it easy, the file is a 32 bit PE file.
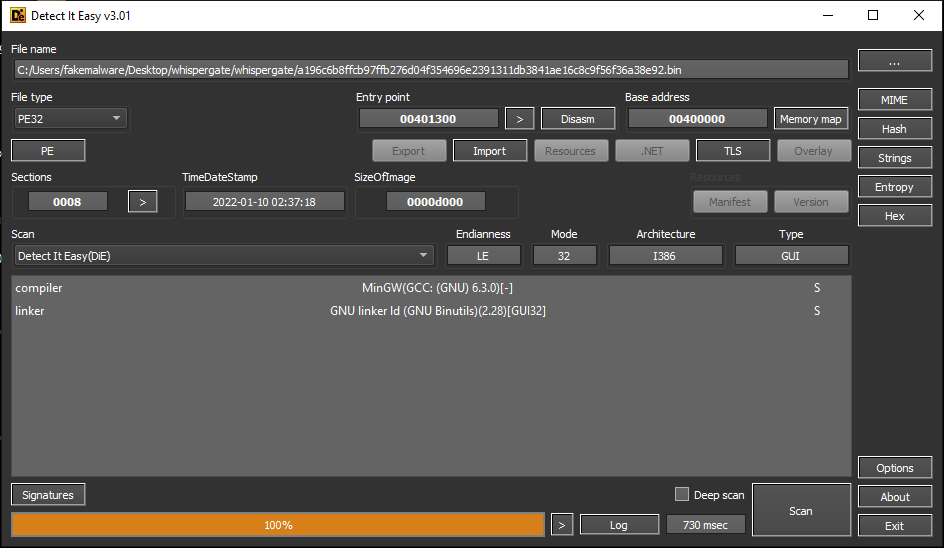 it is compiled and linked using MinGW (GCC 6.3.0) and GNU linker.
it is compiled and linked using MinGW (GCC 6.3.0) and GNU linker.
die shows entropy as 6.07208, which is high but it also says executable is not packed.
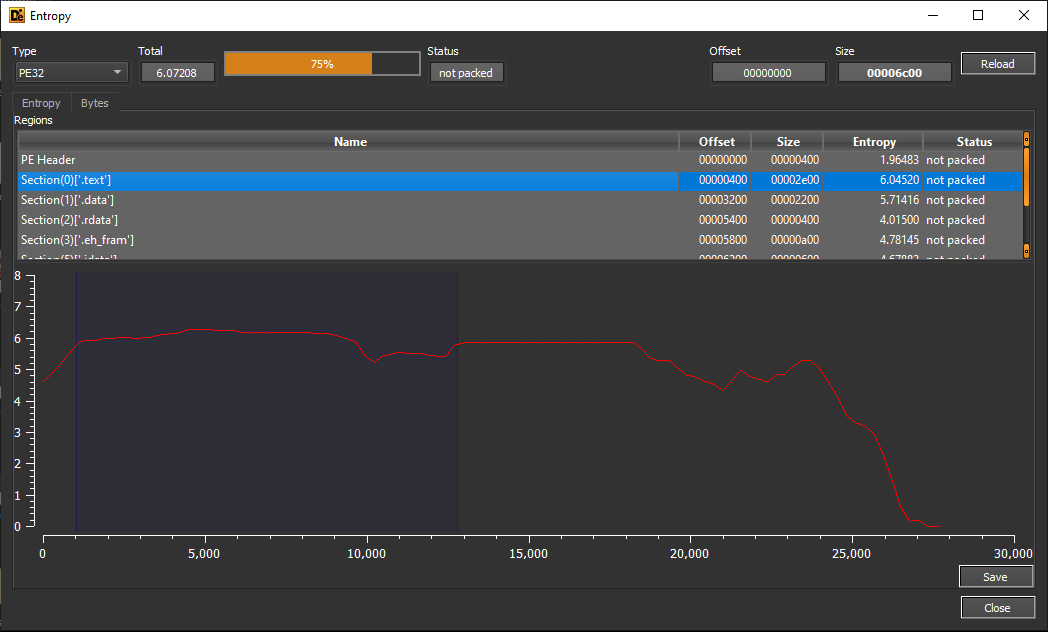 As usual, entropy in the .text section is higher than in the other sections.
As usual, entropy in the .text section is higher than in the other sections.
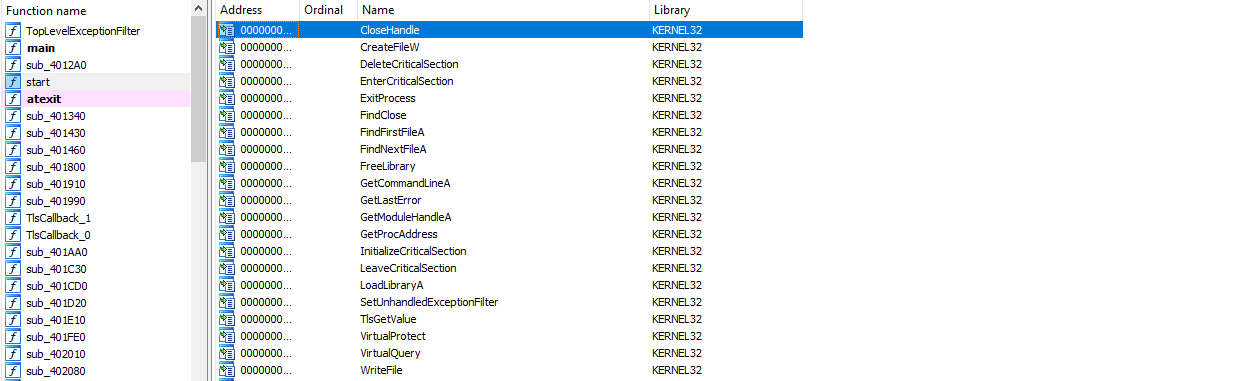
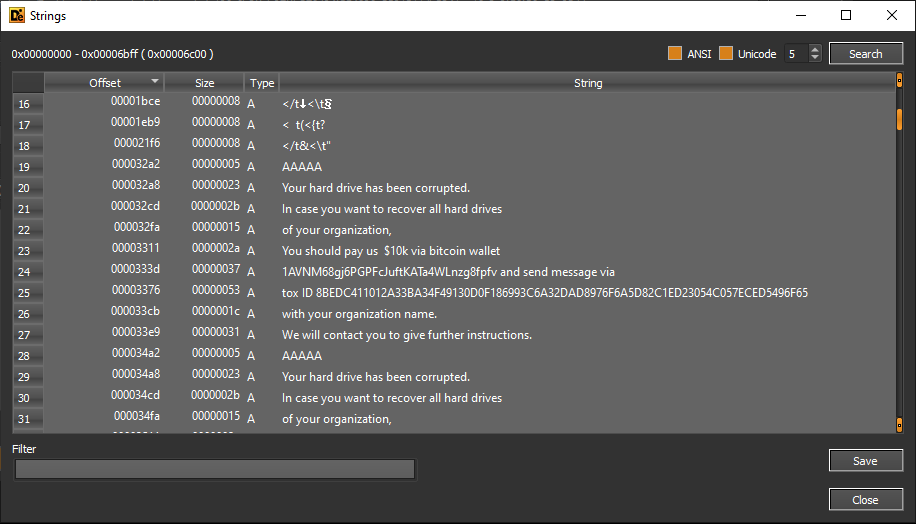 strings in the binary are not encrypted. several strings shown in the above diagram gives hints about
malware’s capabilities such as disk corruption.
strings in the binary are not encrypted. several strings shown in the above diagram gives hints about
malware’s capabilities such as disk corruption.
Also, note that it shows a bitcoin wallet and a tox ID that can be used as signatures.
- 1AVNM68gj6PGPFcJuftKATa4WLnzg8fpfv
- 8BEDC411012A33BA34F49130D0F186993C6A32DAD8976F6A5D82C1ED23054C057ECED5496F65
Executable does not have many imports. There’s no APIs related to cryptography eventhough malware claims to encrypt the files.
Code analysis⌗
IDA shows that PE contains two TLS callbacks. Initially suspected these were for anti-debugging purposes but turns out to be no.
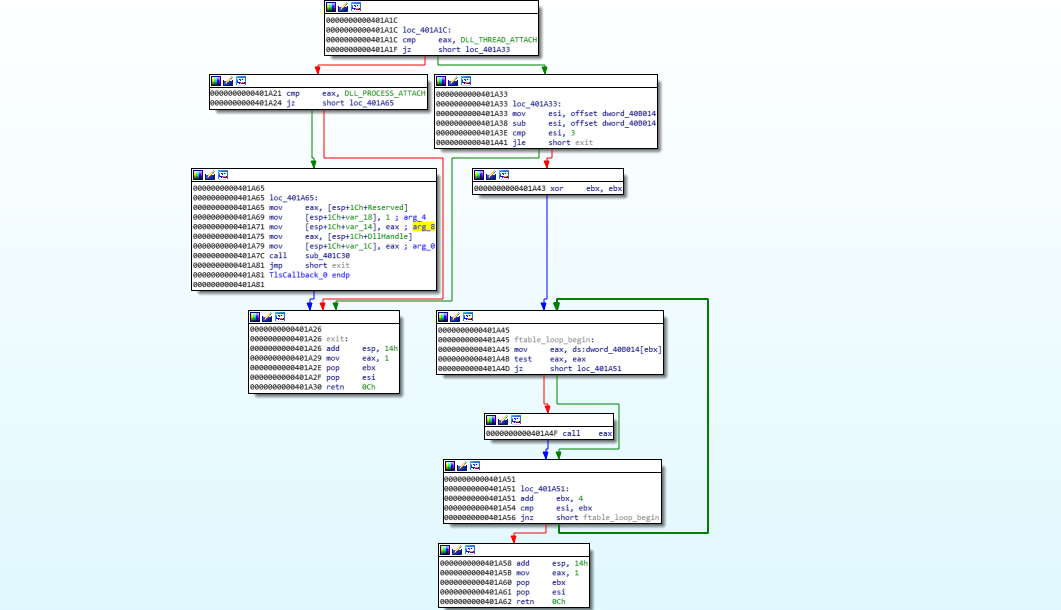 first TLS callback starts calling some function pointers if
first TLS callback starts calling some function pointers if Reason is DLL_THREAD_ATTACH.
 the second TLS callback simply returns if
the second TLS callback simply returns if Reason is something other than DLL_THREAD_DETACH or DLL_PROCESS_DETACH,
suggesting this may be de initializing whatever initialized by the tlscallback1.
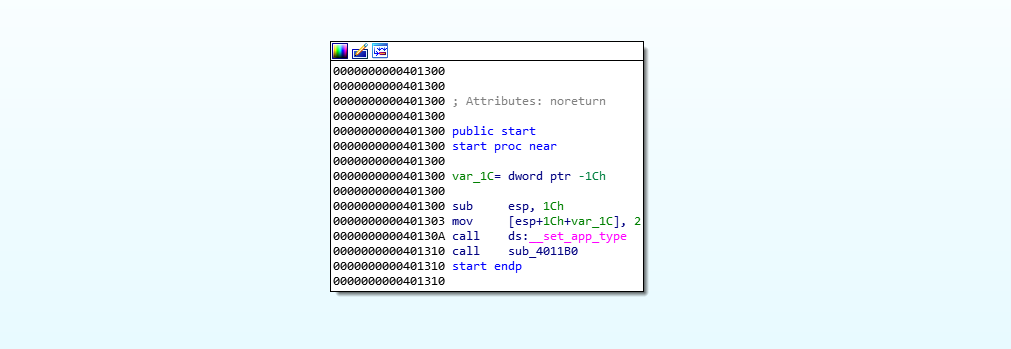 start function calls
start function calls sub_4011b0 after setting the app type.

sub_4011b0 calls function sub_403b60 that is responsible for main functionality of the malware.
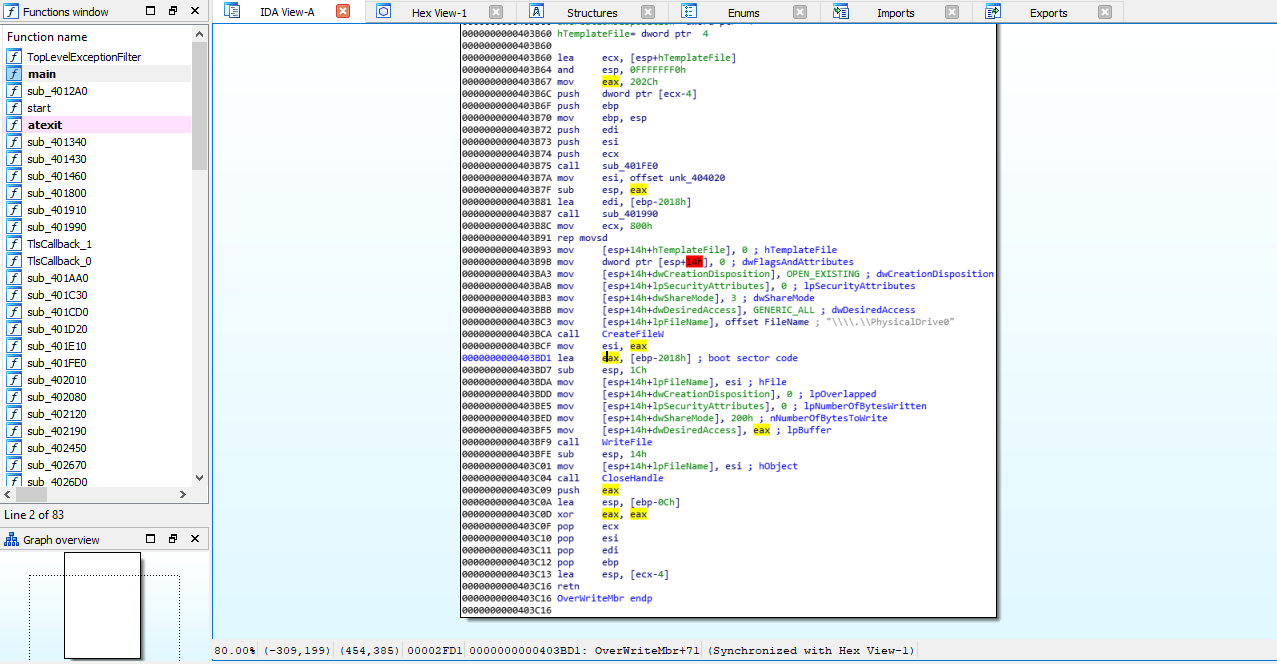 the function copies 2048 bytes at global offset `` into the stack.
the function copies 2048 bytes at global offset `` into the stack.
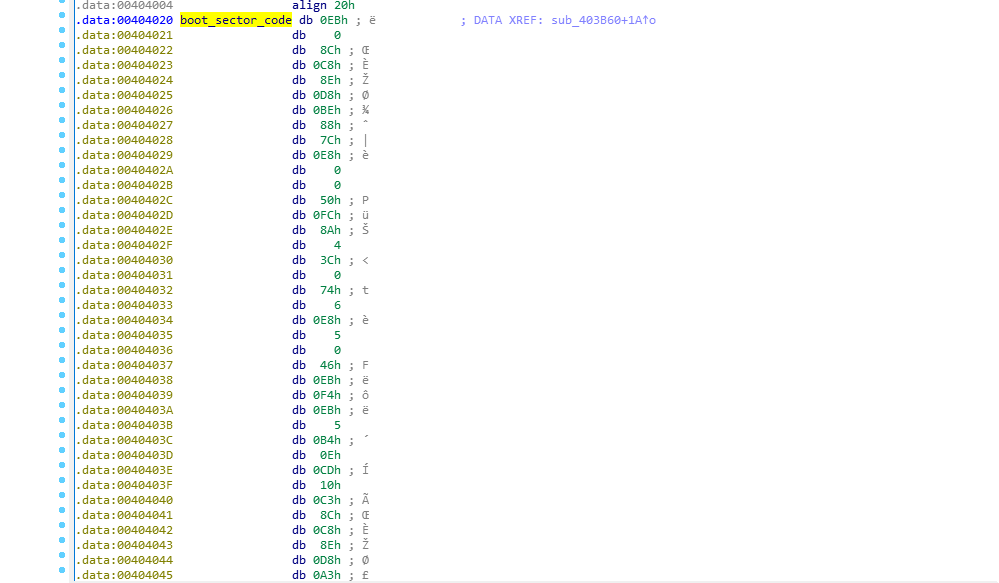
 offset contains bytes of compiled x86 real mode boot sector code, along with the boot signature
offset contains bytes of compiled x86 real mode boot sector code, along with the boot signature 0x55AA.
Then it calls CreateFileW passing \\\\.\\PhysicalDrive0 as filename argument. returned handle is then passed to WriteFile along with the stack buffer that contains boot sector code. If the call is successful, it will overwrite MBR (master boot record) with a custom boot sector.
After BIOS has done selecting the boot device it will load overwritten MBR into memory and the CPU will start executing a parasite bootloader.
Also, note that malware does not encrypt anything.
Extracting boot sector code⌗
 buffer containing boot sector code can be extracted by placing a breakpoint at the address where it is accessed and using the show in dump feature in x32dbg.
buffer containing boot sector code can be extracted by placing a breakpoint at the address where it is accessed and using the show in dump feature in x32dbg.
extracted buffer can be then saved as a raw binary file for further analysis.
Reversing boot sector code⌗
 cs segment register is initially initialized to 0x0, it is used to zero out
cs segment register is initially initialized to 0x0, it is used to zero out ax and set up other segment registers. then loads the ransom note into si register.
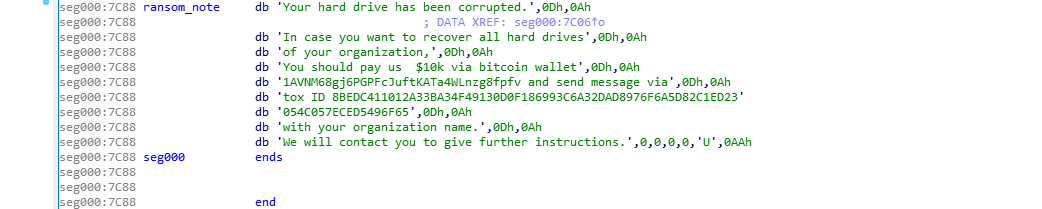
Next instruction calls print_loop, which then calls print_char after loading al with the byte at si. And it will repeat this operation until [si] is null.

print_char uses BIOS interrupts to put a single character into the screen. A BIOS interrupt call is a feature of BIOS that allows bootloaders and early kernels to access BIOS services such as video memory access and low-level disk access. To use BIOS interrupts, ah register should be initialized to the function number. parameters passed down through registers and similar to x86 syscalls, int instruction is used to do the software interrupt along with the BIOS service number
For instance, in the above image, malware loads Display character function number 0x0e into ah and calls
BIOS video service.
More about BIOS interrupts - Ralf Brown’s BIOS interrupt list.
After printing the ransom note, the overwritten code jumps into another label
 which then jumps to label
which then jumps to label corrupt_c
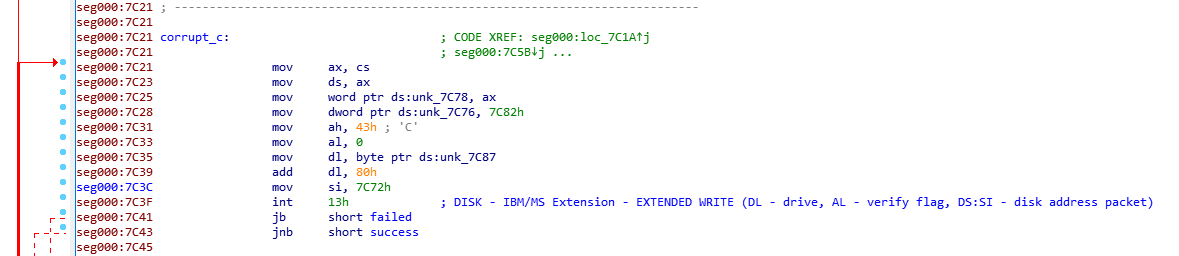 Two insutrctions after segment register initialization sets word at
Two insutrctions after segment register initialization sets word at 0x7c78 to 0x0000 and dword at 0x7c76 to 0x7c82 (‘AAAA’).

This basically initializes the DAP (Disk Address Packet) structure. DAP is a structure that should be initialized in memory in order to use Logical block addressing with interrupt 0x13. This structure is then should be passed through si register.
layout of the structure
Offset Size Description
0 1 size of packet (16 bytes)
1 1 always 0
2 2 number of sectors to transfer (max 127 on some BIOSes)
4 4 transfer buffer (16 bit segment:16 bit offset) (see note #1)
8 4 lower 32-bits of 48-bit starting LBA
12 4 upper 16-bits of 48-bit starting LBA
before the interrupt call int 0x13, which is used for low-level disk access, ah register is initialized to 0x43, BIOS function number for writing sectors to the disk.
following registers are also initialized
al - 0x0 (close clock write)
dl - 0x80 (hard disk)
si - 0x7c72 (DAP)
The si register is loaded with address 0x7c72, which must be the disk address packet.
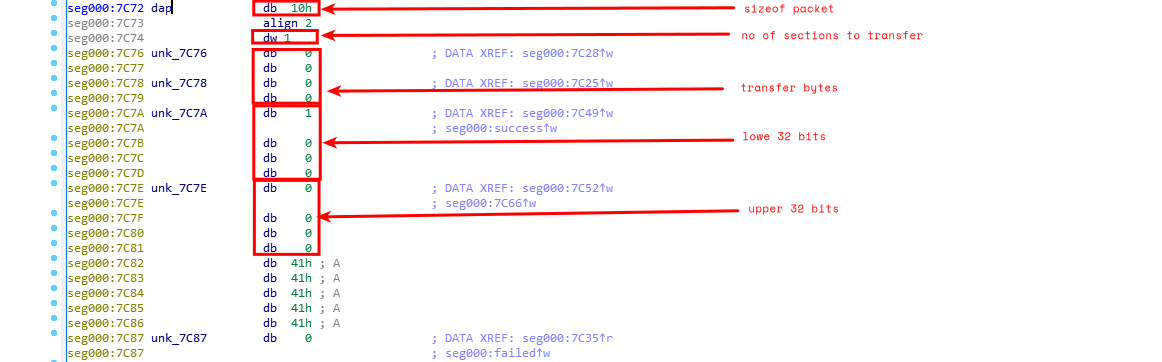
The next few instructions check whether an extended write operation is successful or not. if cf is set (errors) control flow gets redirected to loc_7c45, else, to loc_7c5d.
 at
at loc_7c45, it increments the last element in the byte array by 1 and moves 0x1 to [0x7c7a]. int next instruction zero out [0x7c7e].

loc_7c5d adds 0xc7 to [0x7c7a] and 0x0 [0x7c7e]. clc clears the carry flag.
Both blocks jumps back to corrupt_c.
The loop will continue until the hard disk is completely overwritten by AAAAs.
The end⌗
quick analysis report of WhisperGate stage 01 ends here.
#Spread Anarchy!